
What is Docker?
- “Docker enables apps to be quickly assembled from components
[…]
As a result, IT can ship faster and run the same app, unchanged, on laptops, data center VMs, and any cloud.”https://www.docker.com/whatisdocker/
-
Docker is based on Linux Containers
- Linux Containers utilize a feature of the Linux kernel, cgroups (control groups)
- separate process- and network-space for groups of processes, CPU, memory usage etc. can be restricted
- this technology itself isn't new (e.g. LXC), but Docker improved usability a lot
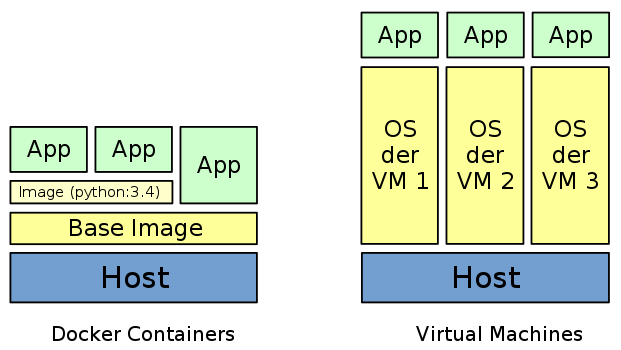
Docker vs. VMs
- Docker containers incur a very small overhead, need very few resources, no time-consuming boot
- different Docker containers share the same image – no virtual HDDs as with VMs
Advantages
- a Docker container can be run on almost every hardware. On the notebook of a developer, a testing or production system, or in the cloud
- containers are “cheap”. Ideal for CI: build container, run tests, discard container
- Docker makes deployment easy. Remedies the problem that e.g. Python projects often aren't easy to deploy and require special knowledge (virtualenv, pip, libjpeg-dev, etc.)
- updating the host system is not problematic anymore (Python or a C-library can be updated without it potentially affecting C-extensions)
- game-changer for PAAS (where the docker daemon can run, containers can be started)
Docker Registry
https://registry.hub.docker.com/
Docker Registry
- Docker offers a lot of images on Docker hub (more than 15000 at the moment)
- there are offical builds, “Trusted builds” und other user-contributed images
- all images build on a base image, very often Ubuntu or Debian → almost no disk space required
- Dockerfiles that are used to build images can be accessed
- it's possible to self-host registries for your own images
docker runautomatically does (docker pull) - downloading the image
/etc/issueshows Debian 7, butuname -rshows Arch Linux (host-OS)- there is one process with PID 1, other processes are forked from this process
- as soon as this process exits, the container shuts down
- it's thus possible to execute a command and have the container shut down immediately afterwards
- this can be used for cron jobs that start a container, for example
docker run
docker run -ti --rm debian:wheezy /bin/bashdocker runcreates a new container from an image-tcreates a pseudo terminal (for output)-igives access to stdin--rmensures that the container is discarded after the main process exits- otherwise the container would be kept on the system and could be restarted with
docker restart
- otherwise the container would be kept on the system and could be restarted with
debian:wheezyis the name of the image, here with tagwheezy. Without a tag:latestwould be used./bin/bashis the command that should be executed by the container. Images usually have a default command that can be overwritten at run-time
Docker Images
- Dockerfiles contain instructions for building a new image
- all images have to be based on a base image (
FROM debian:wheezy) - commands like
RUN apt-get updateare executed in temporary containers, result in layers → layers can be re-used by several images, enable build-caching - local files and folders can be added to the image
- images can be exported as tar files or uploaded into registries
Dockerfile EXPOSE
EXPOSE 80in a Dockerfile opens port 80, for now only for other containersdocker run -p 80:80forwards port 80 to the hostdocker run -p [interface:]80:80binds the port to a certain interface (e.g. localhost)docker run -p 8000:80forwards container port 80 to 8000 on the host
- other containers can access ports that are
EXPOSEd, ifdocker runis called with the--linkparameter
- without
-p 6379:6379the host cannot access the redis instance in the container - other containers can access the port (if
EXPOSEd) with--link
Volumes
- volumes bypass the Docker filesystem, use the filesystem of the host
- volumes make it possible for containers to access the data of other containers
- volumes can be created with
docker run -v, or withVOLUMEin the Dockerfile - other containers can mount the volumes of a container with
--volumes-from - with
docker run -v /local/path:/path/in/containerfiles and folders of the host can be mounted into the container
python3 -m http.serverstarts a development server on port 8000-v $(pwd):/optmounts the current directory into the path /opt in the container
Example Project
- Flask-SSE with Redis, gunicorn and nginx
https://github.com/DazWorrall/flask-sse - normally each process should have it's own Docker container
- containers communicate with each other internally, only nginx is exposed to the host

Flask-SSE
from flask import Flask, render_template, redirect, url_for, json, request
from flask.ext.sse import sse, send_event
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config['SSE_REDIS_HOST'] = 'redis' #default=='localhost'; 'redis' => --link
app.register_blueprint(sse, url_prefix='/events')
@app.route('/new')
def new():
return render_template('message.html')
@app.route('/send', methods=['POST'])
def send():
data = {"message": request.form.get('message', 'Hello, world!')}
send_event("testevent", json.dumps(data), channel='test')
return redirect(url_for('new'))
@app.route('/')
def index():
return render_template('index.html')- https://github.com/DazWorrall/flask-sse/blob/master/example/example.py
- SSE_REDIS_HOST is set to 'redis'
- Flask-SSE example project can be used out of the box otherwise in the container
gunicorn
# python2 due to gevent; wheezy based image, otherwise problems with gevent
# https://github.com/gevent/gevent/issues/513
FROM python:2.7.9-wheezy
MAINTAINER Jesaja Everling <jesaja@everling.email>
ENV MODIFIED_AT 201512061738
RUN pip install gunicorn gevent \
"git+https://github.com/DazWorrall/flask-sse.git"
ADD flask-sse/example /opt/flask-sse
WORKDIR /opt/flask-sse
CMD /opt/flask-sse/run.sh
- pip is used to install gunicorn, gevent and flask-sse
- flask-sse example project is pushed into
/opt/flask-sse- image can be built with
docker build -t flask-sse_gunicorn . - image is tagged with
flask-sse_gunicorn, container can the be started withdocker run flask-sse_gunicorn
- image can be built with
nginx
FROM nginx:1.7.9
ADD default.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
upstream gunicorn {
server flask-sse_gunicorn:5000 fail_timeout=0;
}
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
# http://stackoverflow.com/a/13673298/204706
proxy_set_header Connection '';
proxy_http_version 1.1;
chunked_transfer_encoding off;
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_cache off;
proxy_pass http://gunicorn;
}
}
- in this dockerfile only
default.confis replaced- or:
docker run -v$(pwd)/default.conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf nginx
- or:
- docker containers communicate over an internal network
- other containers can also access e.g.
rediscontainer - Flask-SSE uses redis Pub/Sub to push messages in real-time to clients
Running Containers
docker run -d --name=redis redis:2.8.19--nameis necessary for--link(docker otherwise generates names automatically)
docker run -d --link=redis:redis --name=flask-sse_gunicorn flask-sse_gunicorn--linkcreates a DNS entry forredis, pointing to the IP of the container
docker run -d -p 80:80 --link=flask-sse_gunicorn:flask-sse_gunicorn flask-sse_nginx- only for this container the port is forwarded to the host system
Tips&Tricks
- in Dockerfiles:
apt-get install -y(otherwise user interaction required)ENV MODIFIED_AT(can be changed to deactivate build-cache)
docker execallows to attach to a running container and start a command (e.g./bin/bashfor problem fixing)docker psshows running containers,docker imagesexisting imagesdocker stop/rm $(docker ps -a -q)stops/discards all containersdocker historyshows layers of an imagesystemdunit files orfigcan be used to start inter-dependent containers
Tips&Tricks
- processes in containers by default are run as root!
- Docker containers don't offer the same security as a VM, it's not inherently impossible that an attacker could break out of a container
- either use
USER www-datain the Dockerfile to let a command run as a user, or configure the process accordingly (e.g.user www-data;innginx.conf)
- when working with container IDs, it's sufficient to use the first few characters, e.g.
docker rm 3ec - data-only-containers with
VOLUMEs can be used with--volumes-from, can be migrated withdocker export
Links
- https://registry.hub.docker.com
- https://github.com/wsargent/docker-cheat-sheet
- http://www.nkode.io/2014/08/24/valuable-docker-links.html
- http://www.atlashealth.com/blog/2014/09/persistent-ruby-gems-docker-container
- http://crosbymichael.com/dockerfile-best-practices.html
- http://jonathan.bergknoff.com/journal/building-good-docker-images
- https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tags/docker
- http://www.dockerbook.com